Problem Regions
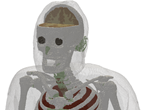
There are various regions in the Visible Human Dataset, where the model is less precise than expected. These regions include areas where the boundaries are very blurred, artifacts exist, or the images are different from what would be expected based on our knowledge of anatomy. For example, reconstructing the homogeneous model shows that the ear lobes look abnormal.
Table 3: Problem Regions (Updated: 2/5/2014)
| Slices | Problem Regions | Why? |
| 1020-1045 | Dura Mater | "Typically, with age, the dura mater thickness changes from 0.3 to 0.8 mm." [14] It is too thick at the top of the head. It is hard to identify and discontinuous elsewhere because of its thickness. |
| 1090-1175 | Sinus Cavities | It is difficult to determine the boundary between the air and the mucous membrane in the sinus cavities. Often, the membrane appears much thicker than it is supposed to be, perhaps because one can see down into the cavity due to the nature of how the images were obtained. Since the membrane is typically less than 1mm thick, it was omitted and the cavities were labeled as air. |
| 1103-1141 | Orbital Cavities | Boundary between fat and bone cortical is difficult to distinguish due to their similar colors. |
| 1107-1122 | Spinal Cord | It is unclear where the spinal cord starts in this set of slices. It is labeled starting in slice 1115. |
| 1109-1133 | Eyes | Boundary between eye sclera and vitreous humor is difficult to distinguish due to their similar colors. |
| 1117-1162 | Nasal Cavities | It is hard to differentiate nasal cavity from bone. The boundaries are not clear due to mucous membrane (which was labeled as air, see sinus cavities). |
| 1127-1142 | Internal Carotid Artery | Region surrounding internal carotid artery is difficult to identify. Currently, the artery is labeled as a blood vessel and is surrounded by air. This is a known error. |
| 1128-1156 | Spinal Cord / Cerebellum | Boundary between spinal cord and cerebellum is very hard to distinguish in this set of slices. |
| 1135-1145 | Temporalis Tendon and Mandible | Difficult to distinguish the transition between the tendon and fat. |
| 1137-1155 | Mucous Membrane | Boundary between mucous membrane and fat is hard to distinguish due to their similar colors. |
| 1148-1229 (Right), 1151-1230 (Left) | Glands near ear canal | The colors are similar between the fat and glands. Additionally, the muscle, fat, and skin boundary is difficult to determine. |
| 1175-1181 (Right), 1180-1184 (Left) | Ear Lobes | Two ear lobes are missing in the model. |
| 1250-1256 | Chin | There is no skin under chin. |
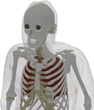
| 1433-1628 | Diaphragm | Boundaries between diaphragm-liver and diaphragm-muscle are difficult to distinguish. |
| 1500-1517 | Esophagus/Aorta | The transition from esophagus to aorta is unclear. |
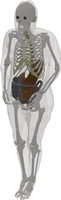
| 1600-1699 | Duodenum | Boundaries between duodenum-stomach and duodenum-small intestine are difficult to distinguish. |
| 1680-1843 | Hands | It is difficult to distinguish the boundaries between the fat, skin, and tendon regions due to their similar colors and complexity. |
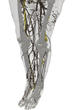
| 2187-2300 | Knees | It is difficult to distinguis the boundaries between the fat, ligament, meniscus, and tendon regions. |
| 2690-2730 | Feet | It is difficult to distinguish the boundaries between the fat, skin, bone, and tendon regions due to their similar colors and complexity. |
| Whole body | Bone Marrow / Bone Cortical | Throughout most of the body, it is difficult to determine the boundary between the bone cortical and bone marrow. This occurs for several reasons: (i) the bone cortical is sometimes very thin. (ii) Efforts were made to label the yellow bone marrow, whose color is similar to bone cortical. |
| Whole body | Blood Vessels | Due to their small nature and complexity, smaller blood vessels were not labeled. This is especially true for the upper part of the body. |
| Whole body | Nerves | Nerves are often similar in color to the tissue that surrounds them and not well labeled in [9]. As a result, the nerves are missing in parts of the body. |
| Whole body | Lymph | The lymphs are often similar in appearance to the tissue that surrounds them. As a result, they are missing in several places. |
| Whole body | Dense Connective Tissue / Tendon / Fat | It is unclear where the boundaries for each of these regions should be. Efforts were made to be consistent and continuous throughout the model. |
| Previous: Tissue Material Assumptions | Up: Assumptions | Next: Electromagnetic Material Properties |